A Dangerous Disease…Don’t be scared.
Aim for better health. There is no cure for diabetes. But it can be managed. Balancing the food you eat with exercise and medicine (if prescribed) will help you control your weight and can keep your blood glucose in the healthy range.
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder in which there is an abnormal increase in the level of glucose or sugar in the blood. Either the body does not produce enough insulin or the insulin that is produced is ineffective. The cause has not been identified.
Who Is likely to Get Diabetes?
Diabetes can affect anyone, but certain groups are higher risk:
- People with a family history
- Obese people
- Hispanic and African American people
- People over the age of 45 years
- Women who have had gestational diabetes or large babies over 9 pounds at birth
- People who live sedentary lifestyles
Type 1 Diabetes
People with Type 1 Diabetes have a lack of insulin in their body because the pancreas fails to produce insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes
When you eat, your food is broken down into a sugar called glucose needed for energy. Your body makes insulin which unlocks cells so they can receive the glucose they need. With type 2 diabetes, your pancreas does not make enough insulin or use it well. This means the glucose stays in your blood.
Having high blood glucose can cause problems like eye, kidney, nerve, and foot disorders. People with diabetes are also at higher risk for high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke, and other serious conditions
Signs & Symptoms
Frequent voiding or passing of urine is called polyuria.
Excessive thirst or drinking which is called polydipsia.
Excessive hunger also known as polyphagia.
Other symptoms include fatigue, frequent infections, and delay in wound healing. it is possible to have diabetes and not know it because the symptoms are not always present. In such cases, the disease develops for a while before it is detected. Sometimes, it is detected too late when other complications have already developed.
Diabetic Care Not too Scary When Done Right
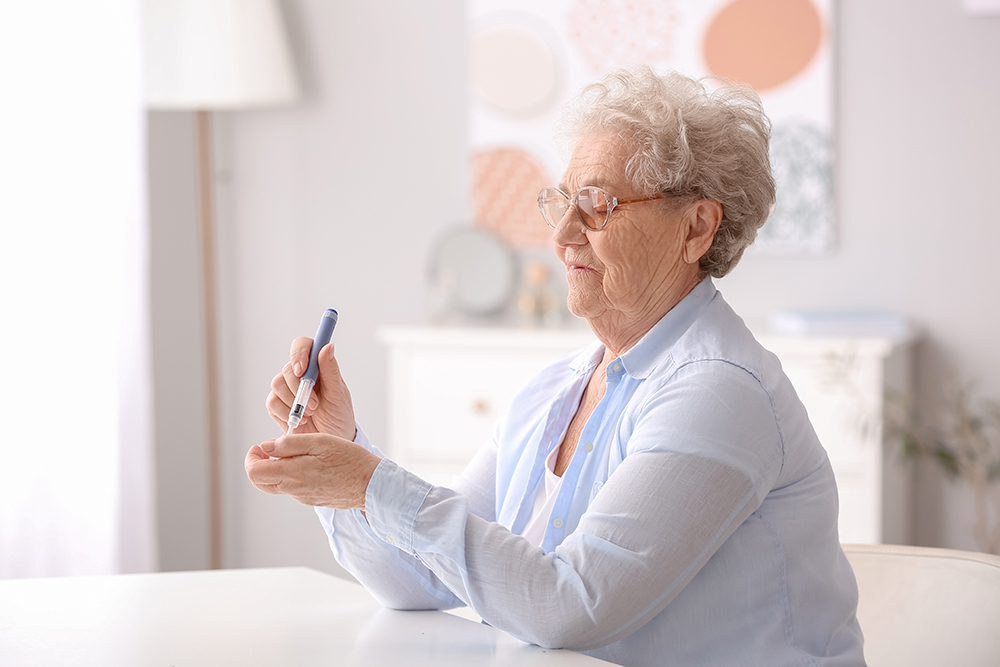
Most diabetics need their blood sugar level tested at least once a day (usually in the morning before breakfast) although some may need their blood sugar tested as much as 5 times per day. The doctor sets the acceptable ranges for each person which may differ from normal ranges in their chart. When a blood glucose level falls outside the range set by the doctor, the doctor must be notified as soon as possible
Question: Why is it important to control Diabetes?
Answer: To avoid deadly complications such as these.
Stroke – heart disease – kidney failure – stomach disease – high blood pressure – eye disease – loss of vision or blindness – nerve damage to hands, feet and legs
Day-To-Day Care:
What, how much, and when to eat. Get active too!
You should change what you eat and how much you eat. Focus less on high-starch foods and eat more fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy and whole grains. Eating better combined with increased activity will encourage weight loss and lead to better blood sugar levels.
Checking blood glucose
Check your blood glucose as your doctor suggests. If you take insulin or diabetes pills, check your blood glucose before exercising. If it is under 100 mg/dl, eat some fruit, crackers, or have a glass of milk or juice. Check it again after exercising to learn how your blood glucose reacts to exercise. Bring a snack if you’ll be out and moving for several hours
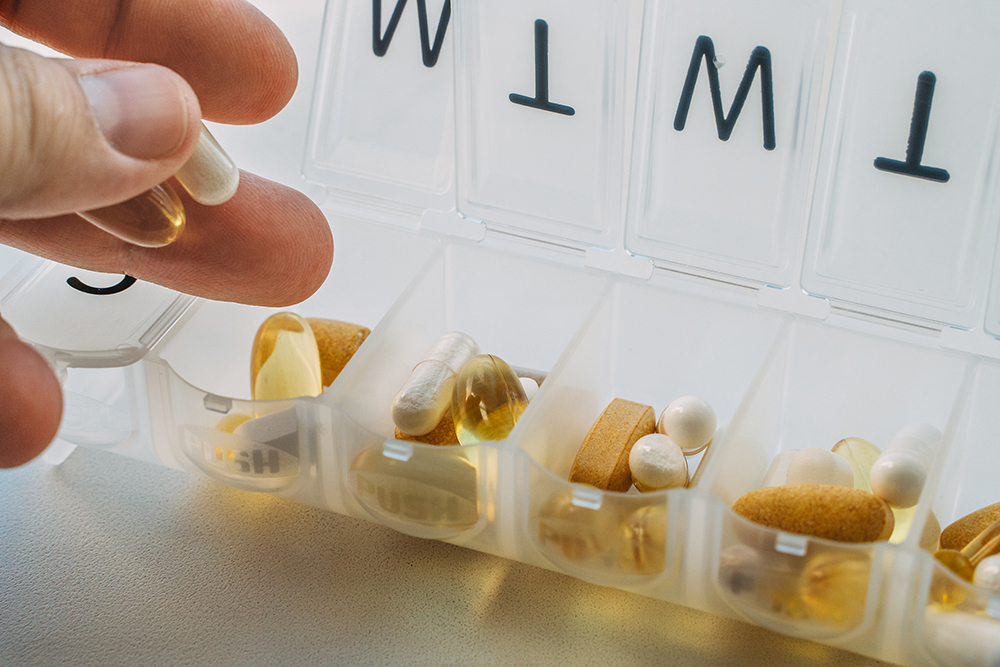
Taking prescribed medicine
Keep an updated list of your medicines (prescription, nonprescription, dietary supplements including vitamins, and herbal remedies). Record important information about each medicine.
- Take all of your medicines exactly as prescribed.
- Use one pharmacy to fill all your prescriptions if possible.
- Keep medicines in a cool, dry place.
- Use a pill organizer.
- Use a reminder timer, an alarm clock, or your mobile phone alarm to remind you when to take medicine.
- Link pill-taking to something in your daily routine (for example, take your medicine right after you brush your teeth).
- Use a chart or dry erase board to keep track of your pill-taking
Other Things You Can Do
- Quit smoking
- Go to your medical appointments
- Learn all you can about diabetes







Comments are closed.